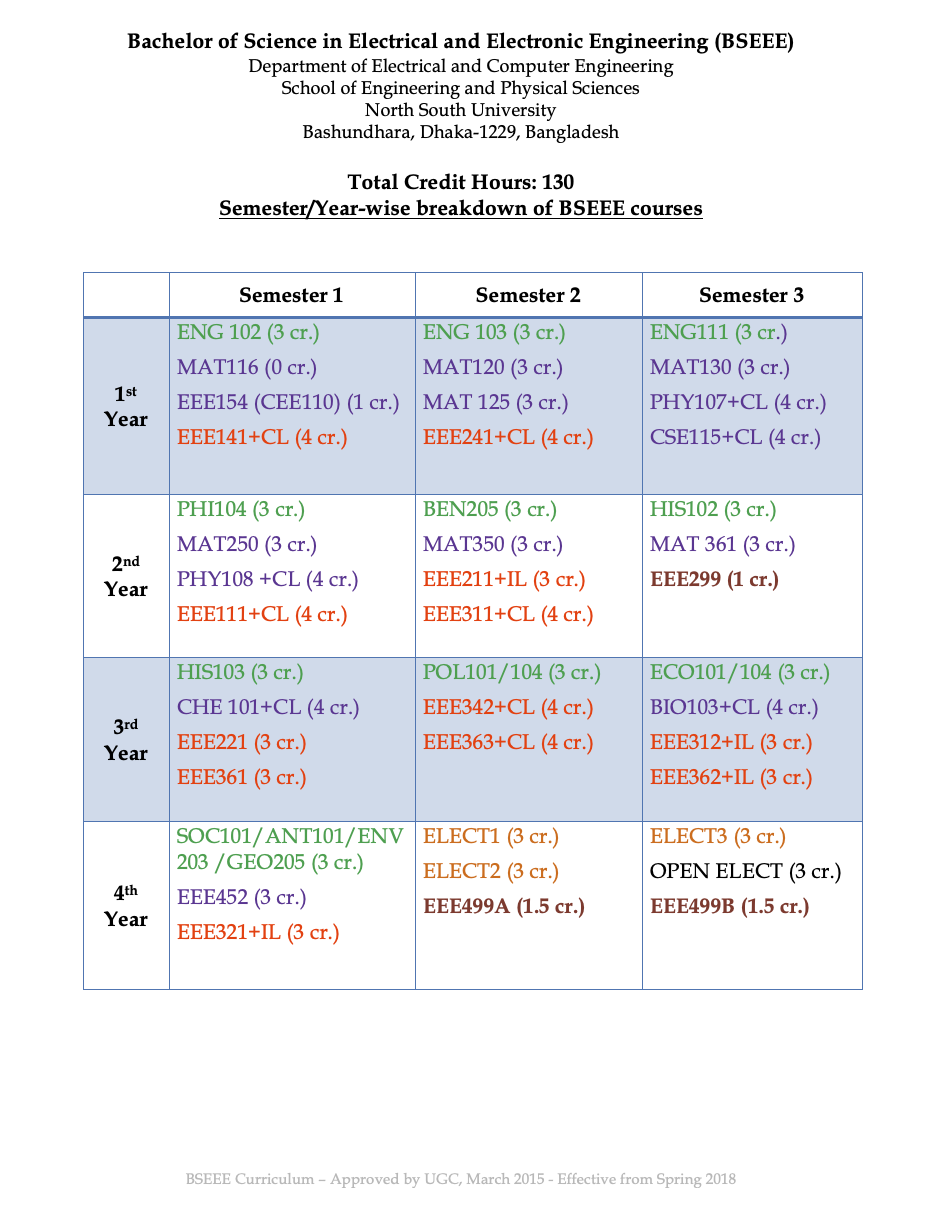
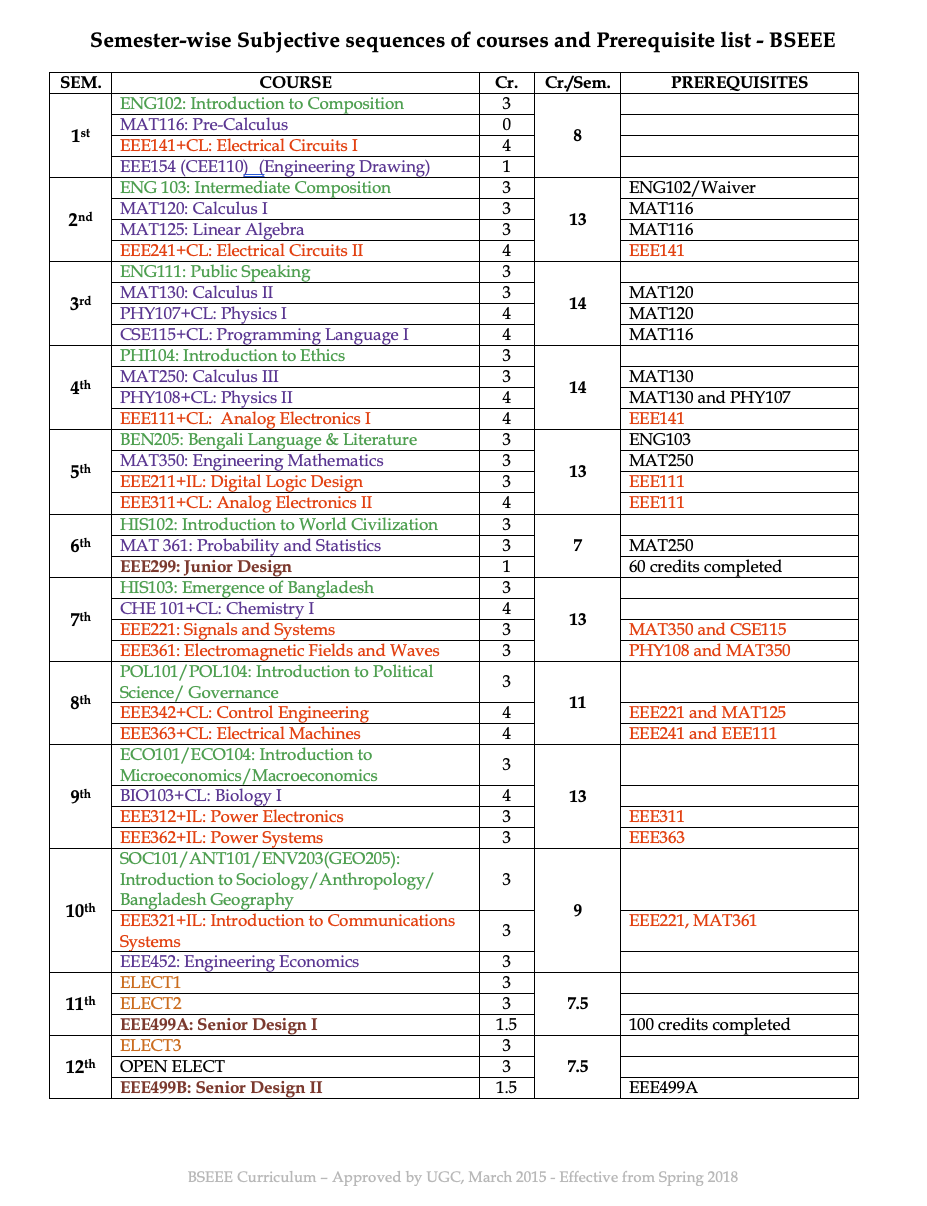
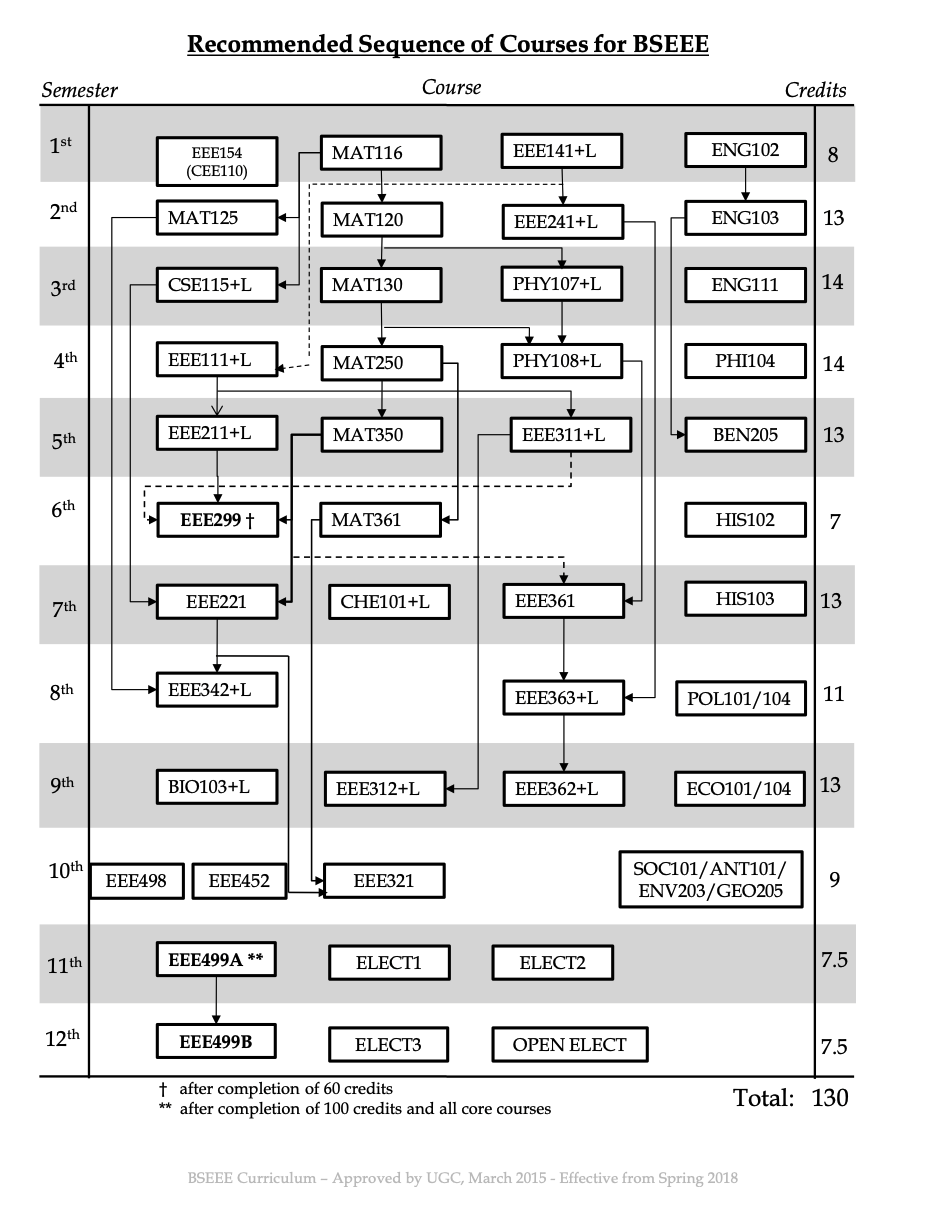
ENG 102 Introduction to Composition
| Code and Name |
ENG 102 Introduction to Composition |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Development of integrated language skills with special focus on the mechanics of the writing process and the study of grammar with an emphasis on syntax. Writing unified, coherent paragraphs with topic sentences and controlling ideas.
ENG 103 Intermediate Composition
| Code and Name |
ENG 103 Intermediate Composition |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
ENG 102/Waiver |
The practice of academic reading and especially writing, focusing on expository essays. Emphasis will be placed on essay structure and editing. Essay types include narrative, descriptive, process, cause and effect, and comparison and contrast.
ENG 111 Public Speaking
| Code and Name |
ENG 111 Public Speaking |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
ENG 103 |
This course introduces students to the fundamental principles and practices of rhetoric. They will learn the art of public speaking which involves persuasion, creative analysis and synthesis of topics, organization, language, delivery, audience awareness and adaptation and the use of supporting materials. Types of speeches will include informative, persuasive, impromptu, inspirational, and special occasion speeches.
PHI 101 Introduction to Philosophy
| Code and Name |
PHI 101 Introduction to Philosophy |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
An exploration of some basic philosophical topics such as the nature of the mind and its relationship to the brain, knowledge, freewill, justice, the existence of God, and mortality. It focuses specially on the nature and function of philosophy. Part or all of the focus of the course may be on the work of one or two philosophers.
PHI 104 Introduction to Ethics
| Code and Name |
PHI 104 Introduction to Ethics |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
This course introduces students to the prominent ethical theories (virtue ethics, utilitarianism, deontology, etc.) in the Western philosophical tradition, examines the debate between moral universalism and moral relativism, and demonstrates various methods of analysis as applied to contemporary moral problems, e.g., abortion, assisted reproductive technologies, organ transplantation, affirmative action, capital punishment, euthanasia, war and violence, gender roles, human rights, environmental degradation. As appropriate, a multicultural perspective on ethical theory and moral problems will be examined.
LBA 101 Bangladesh Culture and Heritage
| Code and Name |
LBA 101 Bangladesh Culture and Heritage |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Deals with the cultural and political heritage of Bangladesh from ancient times to the present and familiarizes students with the cultural milieu of the people to make them aware of Bangladesh’s national identity. Topics include ethnic origin of the people in Bangladesh, religious faiths, festivals, colonial legacy; baul culture; creativity in the arts and crafts; evolution of nationalism in the pre and post-partition East Bengal, Language Movement, struggle for autonomy, and the independence of Bangladesh.
LBA 102 Introduction to World Civilization
| Code and Name |
LBA 102 Introduction to World Civilization |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Focuses on the values and importance of the study of the history of human civilization, especially in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Babylonia; Harappa civilization and the Gandhara civilization, ancient Chinese culture and civilization; ancient Greek civilization, Muslim civilization and their influence over European Renaissance, scientific innovations, cultural progress and religious reformation. The rise of powerful nation states in Europe and North America and the impact of scientific and technological supremacy of the west over the so-called ‘backward communities’ are also studied here.
POL 101 Introduction to Political Science
| Code and Name |
POL 101 Introduction to Political Science |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Provides students with some of the core concepts of political science, such as state, sovereignty, constitutionality, political culture, democracy, political party, civil society and the functioning of major political systems including Bangladesh. It addresses issues, institutions and structures that correspond to our everyday life and shape our political behavior and perceptions as ‘political animal’.
POL 104 Introduction to Governance
| Code and Name |
POL 104 Introduction to Governance |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Introduces students with the concept and various aspects of public governance and their relevance in Bangladesh. Topics includeaccountability, transparency, participation, freedom of information, sound judicial system, capacity building; major governance problems of Bangladesh; role of civil society (including media, NGOs etc.); relationship between better governance and the growth of private sector; donor’s agenda in governance; public sector corruption; implications of e-governance.
ECO 101 Introduction to Microeconomics
| Code and Name |
ECO 101 Introduction to Microeconomics |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
An introduction to the methods and principles of microeconomics. Topics includemarkets; theory of consumer behaviour; production theory; costs of production, and market structure; efficiency in allocation and production.
ECO 104 Introduction to Macroeconomics
| Code and Name |
ECO 104 Introduction to Macroeconomics |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
This course introduces the principles of macroeconomic analysis, its analytical methods with current institutional and empirical issues. Topics include different methods of national income accounting with special emphasis on Bangladesh Economy; issues relating to unemployment, inflation; determination of output, price level, money and banking. It also gives an introductory account of the monetary and fiscal policies; budget and trade deficits; and exchange rate.
SOC 101 Introduction to Sociology
| Code and Name |
SOC 101 Introduction to Sociology |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Provides students with an understanding of the primary phenomena, concepts, issues and practices associated with sociology. Topics include explanation of how societies grow and change; reciprocal effects of economic, political, familial, and scientific institutions on each other and on individual life; changes and social conflict, problems of bureaucratic growth and planned and unplanned social change.
ENV 203/ GEO 205 Introduction to Bangladesh Geography
| Code and Name |
ENV 203/ GEO 205 Introduction to Bangladesh Geography |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Basic geographic concepts and fundamental themes. Geophysical and socio-economic characteristics of Bangladesh; introduction to physical geography; landforms; weather and climate; population geography; cultural and political context; natural resources; economic geography and urban – regional concepts; spatial interaction between human and natural environment.
ANT 101 Introduction to Anthropology
| Code and Name |
ANT 101 Introduction to Anthropology |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Explains the origin of human culture and society and addresses the concepts of fundamental phenomena and procedures of cultural change, impact of culture on personality development, structures of human relationships etc. Students are also introduced to basic research methods that help them develop the primary skills to study human behaviours.
BIO 103 Biology I
| Code and Name |
BIO 103 Biology I |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
4 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Introduction to Biology: Scope, Biology, What is life? and Characteristics of living things; Chemistry of life: Atoms & elements, Molecules & bonds, Electronegativity, Polar & non-polar bonds, Diffusion & osmosis, pH; Biological Macromolecules: Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein and Nucleic acids, Central dogma of molecular biology; Cell structure and function: Organelles description & level of organization; Cellular Reproduction: Cell cycle, Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis; Energy of Life: Cellular respiration (anabolism & catabolism); Enzymes definition and characterization; Photosynthesis; Biological Diversity: Evolution and natural selection, the origin and diversification of life on earth; Evolution of microbes & animals, Classification; Human Physiology: Homeostasis, digestive system, circulatory (blood), excretory and respiratory systems; Health and disease: Food & nutrition; diabetics, cancer and heart disease.
Laboratory Work: Determining the pH of given food/juice/beverage samples, Observing a single cell under light microscope and identification of organelles, Observing bacterial growth from microbial plating, Observing antibiotic activity of saliva/tears, Blood grouping, Determination of serum glucose by glucose oxidase method.
MAT 116 Pre-Calculus
| Code and Name |
MAT 116 Pre-Calculus |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Topics includes sets, real number system, algebraic expressions, systems of equations, functions and relations, quadratic functions, synthetic division, the zeros of a polynomial function, exponential and logarithmic functions, trigonometric functions, graphs of trigonometric functions, analytic trigonometry, additional applications of trigonometry, mathematical induction, the binomial theorem, sequences. Prerequisite: High School Mathematics.
MAT 120 Calculus-I
| Code and Name |
MAT 120 Calculus-I |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 116 |
Covers basic calculus and analytic geometry. Coordinates, Graphs and Lines; Functions and Limits; Differentiations; Application of Differentiation; Integration; Logarithmic and Exponential Functions.
MAT 125 Linear Algebra
| Code and Name |
MAT 125 Linear Algebra |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 116 or an adequate test score |
Basic concepts and techniques of linear algebra; includes system of linear equations, matrices and inverses, determinants, and a glimpse at vector spaces, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, Markov processes.
MAT 130 Calculus II
| Code and Name |
MAT 130 Calculus II |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 120 |
Second course in calculus and analytic geometry. Applications of Definite Integral; Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Trigonometric and Hyperbolic Functions; Techniques of Integration; Improper Integrals: L’Hospitals Rule; Topics of Analytical Geometry; Polar Coordinates and Parametric Equations.
MAT 250 Calculus III
| Code and Name |
MAT 250 Calculus III |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 130 |
Infinite Series; Three Dimensional Vector Spaces; Vector valued Functions; Partial Derivatives: Functions of two variables, limits and continuity, partial derivatives, differentiability and chain rule, directional derivatives and gradients, tangent planes and normal vectors, maxima and minima of functions of two variables. Multiple Integrals: Double integrals, double integrals over non-rectangular regions, double integrals in polar coordinates, triple integrals, centroid, center of gravity, triple integrals in cylindrical and spherical coordinates, change of variables in multiple. Topics in vector calculus: Vector fields, line integrals, Green’s theorem, surface integrals, the divergence theorem, stokes theorem.
MAT 350 Engineering Mathematics
| Code and Name |
MAT 350 Engineering Mathematics |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 250 |
First and Second Order Differential Equations. First order ordinary differential equations, linear differential equations with constant coefficients, Laplace transformations, power-series solutions of differential equations, Bessel functions.
MAT 361 Probability and Statistics
| Code and Name |
MAT 361 Probability and Statistics |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 250 |
Concept of data and variables, collection, tabulation, representation. Measures of central tendencies – mean, median, mode, etc. Measures of dispersion – variance, standard deviation. Random variables and their probability function, binomial probability distribution, mathematical expectation and moment generating functions, joint distribution of two random variables, stochastic independence, continuous random variables, normal distribution, central limit theorem. Programming assignments will be a part of this course.
PHY 107 Physics I
| Code and Name |
PHY 107 Physics I |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
4 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 120 and Physics in HSC/A Level. |
Vectors, Kinematics, Newton’s Law, Conservation of Energy and Momentum, Rotational Kinematics, Conservation of Angular Momentum, Collision, Compton Effect, Nuclear Theory, DeBrogglie, Oscillations and Waves, Gravitation.
The lab component includes: Measurement of length area and volume of solids of regular shapes using vernier caliper, micrometer screw gauge and spherometers. This simple experiment will introduce the students to precision in measurements, error and propagation of error. This knowledge is of fundamental importance, which will be applied in all subsequent experiments, Free fall experiment. To find the time of fall through a given distance and to determine the acceleration of free fall. Apparatus required: Light gates and timer, To study equilibrium of a rigid body. Apparatus needed: force table, pulleys, and weights, To study rectilinear motion on an inclined plane. Apparatus: board, electronic timers or ticker tape timers, light gate etc. Plot of v-t and a-t graphs, To find acceleration of free fall using Atwood’s machine. Apparatus: pulley, known masses and electronic timer, Measurements of the coefficients of static and dynamic friction. Apparatus: wooden blocks, spring balance, known weights etc, Motion of a ball bearing through a resistive medium. To measure the viscosity of glycerin by Stokes’ law. Apparatus: measuring cylinder, stop watch, steel ball bearings, meter rule, and thermometer, Simple harmonic motion 1. Measurement of g by simple pendulum, Simple harmonic motion 2. Vibration of a vertical spring-mass system, measurements of the spring constant and the acceleration of free fall, Study of damped and forced harmonic oscillator. Apparatus: carts, motor, springs, motion sensors etc, Rotational motion. Measurement of moment of inertial of a flywheel, Foucault’s pendulum and the effect of Earth’s rotation, To study the rotational motion of a cylinder down an incline. The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the relationships involving angular acceleration and moments of inertia, Conservation of momentum and kinetic energy in elastic collisions. Apparatus: air track, gliders, light gates, timers etc, Study of one-dimensional inelastic collisions. Apparatus: air track.
PHY 108 Physics II
| Code and Name |
PHY 108 Physics II |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
4 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 240, PHY 107 |
Electric Charge, Coulomb’s Law. The Electric Field: Electric Field Lines, The Electric Field Lines Due to a Point Charge, The Electric Field Lines Due to an Electric Dipole, The Electric Field Lines Due to a Line of Charge, The Electric Field Lines Due to a Charged Disk. Gauss Law: Gauss’s Law in Cylindrical, Planar and Spherical Symmetries. Electric Potential: Equipotential Surfaces, Potential Due to an Electric Dipole. Capacitance: Capacitors in Parallel and Series, Capacitors with a Dielectric. Electric Current, Current Density, Resistance and Resistivity, Ohm’s Law. Circuits, Work, Energy and EMF, Single Loop Circuits, Potential Differences, Multiloop Circuits, RC Circuits. The Magnetic Field, Ampere’s Law, Solenoids and Torroids, Faraday’s Law of Induction, Alternating Currents, Maxwell’s Equations.
The lab components will cover related experiments the topics covered in the theory part.
CHE 101 Chemistry I
| Code and Name |
CHE 101 Chemistry I |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
4 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
This course covers fundamental principles of chemistry. Topics include measurement, atomic and molecular structure, periodicity, chemical reactions, chemical bonding, stoichiometry, thermochemistry, Chemical Equilibrium and Kinetics, gas laws and solutions. This course is appropriate as a basic chemistry course or as a science elective for students who have science, engineering, or mathematics majors. Upon completion, students will be able to- Define chemistry as the study of matter, can apply the basic concepts in their future studies and apply safe laboratory skills to solve problems in a cooperative environment.
Laboratory Work:Â Introducing analytical balance, proving the law of definite proportions, estimation of Avogadro’s number, standardization of HCl, acid Base titration, determination of density.
EEE 452 Engineering Economics
| Code and Name |
EEE 452 Engineering Economics |
| Type |
Required, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Course Summary: Time Value of Money and the Mathematics of Finance, Figures of merit (NPV, IRR, BC, etc) in making engineering design and business decisions. After Tax Analysis (ATA) using the income statement format. Risk analysis and assessment. Financial accounting. Focuses on the key aspects of the modern telecommunications and IT sector management, e.g. services engineering, billing, HR, operations, maintenance, planning, customer relations, supply chain, changing technologies, regulation policies, solution engineering, outsourcing, strategy development. Principles of engineering project management.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- interpret principles of Economics within the context of engineering, technology, and innovation management
- explain estimation of production function, and infer role of technology on Economics of production and functioning of market
- illustrate technology life cycle, nature of innovations , innovation diffusion pattern and management decision making to deal with them.
- explain Telecommunication economics, relate network economics, dynamic competition, and regulation, and interpret their implications on competition scenario of telecom industry
- explain economics of design for manufacturing (DFM)
- explain the concept of financing such as risk and venture capital financing, time value of money, and intangible asset valuation, and relate them to management of technology and innovation projects.
- illustrate principles of project management including planning, scheduling and resource allocation, project budgeting and cost control, and contract management.
CEE 110 Engineering Drawing (EEE 154)
| Code and Name |
CEE 110 Engineering Drawing (EEE 154) |
| Type |
|
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Introduction: lettering, numbering and heading; plane geometry. Projection (Solid Geometry). Development and true shape: cube, pyramid, cone, prism; section and true shape. Isometric drawing, oblique drawing. Plan, elevation and section of engineering structures; reinforcement details of beams, columns, slabs, stairs etc. Introduction to Computer Aided Design (CAD).
CSE 115 Programming Language I
| Code and Name |
CSE 115 Programming language I |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Course Summary: This is the first course in the computer science programming and is required for all computer science and engineering majors. This course introduces the fundamental concepts of structured programming. Topics include fundamentals of computers and number systems, algorithms & flowcharts, fundamental programming constructs: syntax and semantics of a higher-level language, variables, expressions, operators, simple I/O to console and files, conditional and iterative control structures, functions and parameter passing, dynamic memory allocation; fundamental data structures: arrays, structures, strings and string processing; and testing and debugging strategies.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- learn fundamental knowledge on basics of computers, hardware, software, and number systems,
- familiarize about the basic terminologies used in computer programming,
- proficiently transform designs of problem solutions into a standard programming language,
- use an integrated development environment (IDE) to write, compile, and execute programs involving a small number of source files,
- proficiently use fundamental programming elements including: variable declaration, data types and simple data structures (arrays, strings, and structures), decision structures, loop structures, functions/methods, input and output for console and text files,
- apply debugging and testing techniques to locate and resolve errors and to determine the effectiveness of a program, and
- have understanding of professionalism, codes of ethics and responsible conduct.
EEE 111/ ETE 111 Analog Electronics-I
| Code and Name |
EEE 111/ ETE 111 Analog Electronics-I |
| Type |
Required, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 141/ETE 141 Electrical Circuits-I |
Course Summary: In this course, a variety of electronic devices used in the design of analog electronics are studied. Basic understanding of semiconductor devices is covered. Emphasis is placed on diodes, BJT, and FET. Small and large signal characteristics and models of electronic devices, analysis and design of elementary electronic circuits are also included. This course has separate mandatory laboratory sessions every week as EEE 111L.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to possess a solid understanding of semiconductor devices used in the design of analog electronics
- to learn the required skill to use the electronic devices in designing practical circuits to solve practical problems.
- to gain the ability of conduct, analyze, and interpret experiments, and apply experimental results to improve processes or circuit systems.
EEE 111L/ ETE 111L Analog Electronics-I Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 111L/ ETE 111L Analog Electronics-I Lab |
| Type |
Required, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 141/ETE 141 Electrical Circuits-I |
Course Summary: In this course, a variety of electronic devices used in the design of analog electronics are studied. Basic understanding of semiconductor devices is covered. Emphasis is placed on diodes, BJT, and FET. Small and large signal characteristics and models of electronic devices, analysis and design of elementary electronic circuits are also included. This course has separate mandatory laboratory sessions every week as EEE 111L.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to possess a solid understanding of semiconductor devices used in the design of analog electronics
- to learn the required skill to use the electronic devices in designing practical circuits to solve practical problems.
- to gain the ability of conduct, analyze, and interpret experiments, and apply experimental results to improve processes or circuit systems.
EEE 141 Electrical Circuits I
| Code and Name |
EEE 141 Electrical Circuits I |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 120 (Calculus and Analytic Geometry I) |
Course Summary: Formulation and solution of circuit equations using various circuit analysis techniques including Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, mesh and nodal analysis, superposition, source conversion, Thevenin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, and maximum power transfer theorem. Then transient analysis of series RC and RL circuits will be discussed followed by brief introduction of capacitors and inductors. This course has a separate mandatory laboratory session every week as EEE 141L.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce basic circuit laws applied in simple DC circuits to compute voltage, current, equivalent resistance and power.
- to analyze complex circuits using nodal and mesh methods.
- to simplify circuit analysis using various circuit theorems.
- to examine the transient analysis of series RC and RL circuits.
- to enable the students to build circuits and conduct experiments on it in a laboratory setting.
EEE 141L Electrical Circuits I Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 141L Electrical Circuits I Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 120 (Calculus and Analytic Geometry I) |
Course Summary: Formulation and solution of circuit equations using various circuit analysis techniques including Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, mesh and nodal analysis, superposition, source conversion, Thevenin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, and maximum power transfer theorem. Then transient analysis of series RC and RL circuits will be discussed followed by brief introduction of capacitors and inductors. This course has a separate mandatory laboratory session every week as EEE 141L.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce basic circuit laws applied in simple DC circuits to compute voltage, current, equivalent resistance and power.
- to analyze complex circuits using nodal and mesh methods.
- to simplify circuit analysis using various circuit theorems.
- to examine the transient analysis of series RC and RL circuits.
- to enable the students to build circuits and conduct experiments on it in a laboratory setting.
EEE 211 Digital Logic Design
| Code and Name |
EEE 211 Digital Logic Design |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
CSE173 Discrete Mathematics |
Course Summary: This course provides an introduction to logic design and basic tools for the design of digital logic systems. A basic idea of number systems will be provided, followed by a discussion on combinational logic: logic gates, Boolean algebra, minimization techniques, arithmetic circuits (adders, subtractors), basic digital circuits (decoders, encoders, multiplexers, shift registers), programmable logic devices (PROM, PAL, PLA). The course will then cover sequential circuits: flip-flops, state transition tables and diagrams, state minimization, state machines, design of synchronous/asynchronous counters, RAM/ROM design. An introduction to programmable logic will also be provided. Hands-on experience will be provided through project on design of a sequential logic system. This course has separate mandatory laboratory session every week as CSE 231L.
Course Objective: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce Boolean logic operation and Boolean Algebra
- to teach students how to use Boolean Algebra and K-maps to realize two-level minimal/optimal combinational circuits
- to exposed students in the introductory design process of combinational and sequential circuits
- to teach the operation of latches, flip-flops, counters and registers.
- to explain how to analyze and design sequential circuits built with various flip-flops.
- to introduce using simulation tool for digital system design.
EEE 211L Digital Logic Design Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 211L Digital Logic Design Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
0 |
| Pre-requisites |
CSE173 Discrete Mathematics |
Course Summary: This course provides an introduction to logic design and basic tools for the design of digital logic systems. A basic idea of number systems will be provided, followed by a discussion on combinational logic: logic gates, Boolean algebra, minimization techniques, arithmetic circuits (adders, subtractors), basic digital circuits (decoders, encoders, multiplexers, shift registers), programmable logic devices (PROM, PAL, PLA). The course will then cover sequential circuits: flip-flops, state transition tables and diagrams, state minimization, state machines, design of synchronous/asynchronous counters, RAM/ROM design. An introduction to programmable logic will also be provided. Hands-on experience will be provided through project on design of a sequential logic system. This course has separate mandatory laboratory session every week as CSE 231L.
Course Objective: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce Boolean logic operation and Boolean Algebra
- to teach students how to use Boolean Algebra and K-maps to realize two-level minimal/optimal combinational circuits
- to exposed students in the introductory design process of combinational and sequential circuits
- to teach the operation of latches, flip-flops, counters and registers.
- to explain how to analyze and design sequential circuits built with various flip-flops.
- to introduce using simulation tool for digital system design.
EEE 221 Signals and Systems
| Code and Name |
EEE 221 Signals and Systems |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
MAT 350 |
Course Summary: This course provides an introduction to the analysis techniques for different signals and systems. It includes signal representations including Fourier and Laplace transforms. System definitions and properties, such as linearity, causality, time invariance, and stability are covered. This course also includes convolution, delta function, transfer functions and frequency response to determine system characteristics. This course has separate mandatory laboratory session every week as EEE 221L. Lab classes cover the operations with different signals and their distinct representations by using the simulation tool MATLAB.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce different signal operations, distinct systems and their applications.
- to use delta function and convolution integrals for engineering problems.
- to expose students in the physical world/ real world problems of signals and systems such as applications and differences of Fourier series and Fourier transform.
- to analyse complex engineering problems such as the determination of system response, time and frequency domain analysis and the application of the properties of Fourier and Laplace transform.
- to introduce MATLAB for simulation platform.
EEE241/ETE241 Electrical Circuits II
| Code and Name |
EEE241/ETE241 Electrical Circuits II |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE141/ETE141 – Electrical Circuits |
Course Summary: Formulation and solution of circuit equations, network theorems, sinusoidal steady-state analysis. Topics include loop and nodal analysis, superposition and Thevenin’s theorem, properties of sinusoids, phasor representation and vector diagrams. AC Power concepts and Applications, Power Factor Correction, Three Phase Circuits, Power in Three Phase Circuits, Mutual Inductance, Transformers, Usc of MATLAB and PSpice for AC Circuit Analysis. This course has mandatory laboratory sessions every week. This course has separate mandatory laboratory sessions every week in a separate course EEE241L/ETE241L.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- acquire solid understanding of basic ac circuit concepts.
- apply basic laws, known as Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s laws to simple ac circuits
- learn techniques in analyzing series, parallel, and series-parallel ac circuits.
- know different theorems for network analysis applied to ac circuits.
- gain ac power concepts and practical applications of these concepts.
- analyze balanced and unbalanced three-phase circuits.
- use computer-aided design tools for circuit analysis of AC circuits.
EEE241L/ETE241L Electrical Circuits II Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE241L/ETE241L Electrical Circuits II Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE141/ETE141 – Electrical Circuits |
Course Summary: Formulation and solution of circuit equations, network theorems, sinusoidal steady-state analysis. Topics include loop and nodal analysis, superposition and Thevenin’s theorem, properties of sinusoids, phasor representation and vector diagrams. AC Power concepts and Applications, Power Factor Correction, Three Phase Circuits, Power in Three Phase Circuits, Mutual Inductance, Transformers, Usc of MATLAB and PSpice for AC Circuit Analysis. This course has mandatory laboratory sessions every week. This course has separate mandatory laboratory sessions every week in a separate course EEE241L/ETE241L.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- acquire solid understanding of basic ac circuit concepts.
- apply basic laws, known as Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s laws to simple ac circuits
- learn techniques in analyzing series, parallel, and series-parallel ac circuits.
- know different theorems for network analysis applied to ac circuits.
- gain ac power concepts and practical applications of these concepts.
- analyze balanced and unbalanced three-phase circuits.
- use computer-aided design tools for circuit analysis of AC circuits.
EEE 299 Junior Design Project I
| Code and Name |
EEE 299 Junior Design Project I |
| Type |
Core, Engineering |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
60 Credits Completed |
Course Summary: This is an intermediate level design course, after a student has gathered sufficient experiences on laboratory equipments and knowledge of engineering applications up to 200 level core courses, core math, and core science courses. This “Junior Design Course” involves multidisciplinary teams of students who build and test custom designed systems, components or engineering processes. Design projects selected from proposal submitted by the students, or recommended by faculty, or text book design problems. The instructor acts as supervisor and assists them in design team formation and organization, design proposal preparation, implementation of design process, project scheduling and management, design reviews, design simulation and testing, preparation of drawings, specifications, etc. Performances are evaluated by oral presentation of proposal and demonstration of completed projects, report writing, effective use of visual aids, design process, project management and scheduling etc.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- implement a specific design problem on engineering applications
- find appropriate method of analysis and design tools to perform design tasks
- create environment for taking journal notes and maintain teamwork in group environment
- gain skills on writing proposal and completed project reports, presentation and demonstration of completed project
- train how to manage finance and scheduling of time while working in multidisciplinary team
EEE311/ ETE311 Analog Electronics II
| Code and Name |
EEE311/ ETE311 Analog Electronics II |
| Type |
Required, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 111/ETE 111 Analog Electronics I |
Course Summary: Design methods to fix gain and bandwidth specifications in amplifiers are presented. Design use of feedback technique is presented. Properties and design amplification of operational amplifiers are studied. Emphasis is given on electronic circuitry used in communication engineering.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce differential amplifier and use of that in operational amplifier, basics of operational amplifier and all special types of circuits using Op-Amp, offset voltage and current, and frequency response of operational amplifier.
- to teach student function of Op-Amps in 555 Timer and different types of modes of operation of 555 Timer.
- to explain regenerative and degenerative feedback systems, different types of negative feedback topologies, the differences between positive feedback and oscillator circuits, the oscillation criteria, different types of sinusoidal oscillator circuits and their working principle.
- tofamiliarize students about passive and active filters, relationship in between roll-offs and cut-off frequency and different types of filter circuits.
- simulateand evaluate the performance analysis of operational amplifiers, Timer circuits, feedback circuits, and oscillator and filter circuits through MultiSim Software.
EEE 311L/ETE 311L Analog Electronics II Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 311L/ETE 311L Analog Electronics II Lab |
| Type |
Required, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 111/ETE 111 Analog Electronics I |
Course Summary: Design methods to fix gain and bandwidth specifications in amplifiers are presented. Design use of feedback technique is presented. Properties and design amplification of operational amplifiers are studied. Emphasis is given on electronic circuitry used in communication engineering.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce differential amplifier and use of that in operational amplifier, basics of operational amplifier and all special types of circuits using Op-Amp, offset voltage and current, and frequency response of operational amplifier.
- to teach student function of Op-Amps in 555 Timer and different types of modes of operation of 555 Timer.
- to explain regenerative and degenerative feedback systems, different types of negative feedback topologies, the differences between positive feedback and oscillator circuits, the oscillation criteria, different types of sinusoidal oscillator circuits and their working principle.
- tofamiliarize students about passive and active filters, relationship in between roll-offs and cut-off frequency and different types of filter circuits.
- simulateand evaluate the performance analysis of operational amplifiers, Timer circuits, feedback circuits, and oscillator and filter circuits through MultiSim Software.
EEE 312 Power Electronics
| Code and Name |
EEE 312 Power Electronics |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 211, MAT 350 |
Course Summary: This introductory course will give an overview of the major aspects of power electronics. Emphasis will be given on basic theoretical methods of calculation and design of important power electronic circuits such as: ac to dc uncontrolled and controlled rectifiers, ac voltage controllers, dc-dc converters, dc to ac inverters and power supplies. The course will also cover power semiconductor devices and wide application aspects of power electronic circuits using diodes, SCR, GTO, BJT, MOSFET, IGBT, rectifiers and switching circuits.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce power semiconductor devices, their switching principles and applications.
- to explain the operation of AC-DC uncontrolled and controlled rectifier, DC-DC converters and DC-AC inverters.
- to analyse the power electronic switch based rectifier, converters and inverters.
- to introduce hardware tools for implementation of power electronic circuits.
EEE 312L Power Electronics Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 312L Power Electronics Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
0 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 211, MAT 350 |
Course Summary: This introductory course will give an overview of the major aspects of power electronics. Emphasis will be given on basic theoretical methods of calculation and design of important power electronic circuits such as: ac to dc uncontrolled and controlled rectifiers, ac voltage controllers, dc-dc converters, dc to ac inverters and power supplies. The course will also cover power semiconductor devices and wide application aspects of power electronic circuits using diodes, SCR, GTO, BJT, MOSFET, IGBT, rectifiers and switching circuits.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce power semiconductor devices, their switching principles and applications.
- to explain the operation of AC-DC uncontrolled and controlled rectifier, DC-DC converters and DC-AC inverters.
- to analyse the power electronic switch based rectifier, converters and inverters.
- to introduce hardware tools for implementation of power electronic circuits.
EEE 321 Introduction to Communications Systems
| Code and Name |
EEE 321 Introduction to Communications Systems |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 221, MAT 361 |
Course Summary: Introduction to basic concepts of communication systems; modulation and demodulation techniques, analog modulation: AM, FM, PM, Digital communication techniques and their merits/demerits; noise in communication system; Overview of modern communication systems, PSTN- Switching functions and Traffic analysis.
Course Objectives: The course objectives of this course are to
- expose students to various classical analog transmission techniques and modern digital communication systems and provide them with the understanding of traffic analysis.
- familiarize with the Digital communication systems and their advantage over analog counterpart.
- learn about the analog to digital conversion process and various encoding techniques: ASK, FSK, PSK. Understand the application of ‘Nyquist’ and ‘Shannon’ capacity formula.
- analyze the behavior of digital communication system under the presence of noise and to equip students with the knowledge of resource calculation through traffic analysis.
- introduce modern day cellular communication system and related phenomena.
EEE 321L Introduction to Communications Systems Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 321L Introduction to Communications Systems Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
0 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 221, MAT 361 |
Course Summary: Introduction to basic concepts of communication systems; modulation and demodulation techniques, analog modulation: AM, FM, PM, Digital communication techniques and their merits/demerits; noise in communication system; Overview of modern communication systems, PSTN- Switching functions and Traffic analysis.
Course Objectives: The course objectives of this course are to
- expose students to various classical analog transmission techniques and modern digital communication systems and provide them with the understanding of traffic analysis.
- familiarize with the Digital communication systems and their advantage over analog counterpart.
- learn about the analog to digital conversion process and various encoding techniques: ASK, FSK, PSK. Understand the application of ‘Nyquist’ and ‘Shannon’ capacity formula.
- analyze the behavior of digital communication system under the presence of noise and to equip students with the knowledge of resource calculation through traffic analysis.
- introduce modern day cellular communication system and related phenomena.
EEE 342 Control Engineering
| Code and Name |
EEE 342 Control Engineering |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 221 |
Course Summary: This course introduces the basics of systems, modeling and control. Focusing on linear and time-invariant systems, this course provides analytical tools to evaluate stability and performance (transient and steady state response) of those systems. It considers systems represented in frequency domain (transfer function) as well as time-domain (differential equations, state-space representations). Various design tools are taught including PID controllers.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to acquaint the students with basic methods of modeling of electrical, mechanical and other dynamic systems.
- to introduce analysis techniques of linear time-invariant systems (LTI) in both time-domain and frequency-domain.
- to introduce control techniques to design a feedback control system in both time-domain and frequency-domain.
- to provide graphical analysis and design tools such as pole zero maps, block diagram reduction, Bode Plots, Root Locus – all applied to examples of real-world systems.
- to instill simulation (eg. Simulink, MATLAB) and hardware skills with application to control engineering.
EEE 342L Control Engineering Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 342L Control Engineering Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 221 |
Course Summary: This course introduces the basics of systems, modeling and control. Focusing on linear and time-invariant systems, this course provides analytical tools to evaluate stability and performance (transient and steady state response) of those systems. It considers systems represented in frequency domain (transfer function) as well as time-domain (differential equations, state-space representations). Various design tools are taught including PID controllers.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to acquaint the students with basic methods of modeling of electrical, mechanical and other dynamic systems.
- to introduce analysis techniques of linear time-invariant systems (LTI) in both time-domain and frequency-domain.
- to introduce control techniques to design a feedback control system in both time-domain and frequency-domain.
- to provide graphical analysis and design tools such as pole zero maps, block diagram reduction, Bode Plots, Root Locus – all applied to examples of real-world systems.
- to instill simulation (eg. Simulink, MATLAB) and hardware skills with application to control engineering.
EEE 361/ ETE 361 Electromagnetic Fields & Waves
| Code and Name |
EEE 361/ ETE 361 Electromagnetic Fields & Waves |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
PHY 108, MAT 350 |
Course Summary: This course provides an introduction to Maxwell’s equations and their applications to engineering problems. Topics include the physical meaning of Curl, Gradient and Divergence; physical meaning of Maxwell’s point relations along with Maxwell’s integral relations, Electrostatics, magnetostatics, time-varying fields, waves and propagation, force, energy, oblique incidence of light, boundary conditions, Poynting vector, cavity, different co-ordinate systems and antennas.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are
- to introduce Maxwell’s equations, their physical meaning and applications.
- to use Curl, Gradient and Divergence for electromagnetic and real world problems.
- to expose students in the real world problems of electromagnetism such as application
- of interface/boundary conditions.
- to be familiar with the electrostatics and magnetostatics along with time varying fields and waves.
- to analyse complex theoretical problems such as waves and propagation, oblique incidence of light, Poynting vector and boundary conditions.
- to introduce with cavity (or waveguides) and antenna analysis.
EEE 362 Power Systems
| Code and Name |
EEE 362 Power Systems |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 241 |
Course Summary: Phasors, complex power, voltage regulation; balanced/unbalanced three-phase operation, short circuit capacity, circuit breakers; transmission lines, series/shunt impedance, short, medium, and long line models; symmetrical components, sequence networks.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- learn fundamentals concepts of phasor analysis, complex power, three-phase power systems, balanced and unbalanced operation, per unit method, one line diagram.
- familiar with analytical models of transformers, generators and transmission lines.
- learn working principles and operation of three-phase transformers, autotransformers
- gain knowledge on different analytical tools related to electric power transmission and distribution
EEE 362L Power Systems Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 362L Power Systems Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
0 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 241 |
Course Summary: Phasors, complex power, voltage regulation; balanced/unbalanced three-phase operation, short circuit capacity, circuit breakers; transmission lines, series/shunt impedance, short, medium, and long line models; symmetrical components, sequence networks.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- learn fundamentals concepts of phasor analysis, complex power, three-phase power systems, balanced and unbalanced operation, per unit method, one line diagram.
- familiar with analytical models of transformers, generators and transmission lines.
- learn working principles and operation of three-phase transformers, autotransformers
- gain knowledge on different analytical tools related to electric power transmission and distribution
EEE 363 Electrical Machines
| Code and Name |
EEE 363 Electrical Machines |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lecture |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 241 |
Course Summary: Working principles and applications of various DC and AC machines such as Dc generator/motor, Alternator, Synchronous motor, Induction motor and transformer, Armature winding diagram, Torque-Speed characteristics, power flow diagram, Parallel operation of generator, House diagram, and controlling motor characteristics.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- make students conversant with the concepts of various types of electrical machines and their applications.
- explain the operation principle of transformer. .
- gain knowledge about the principle of operation of DC generator and their constructions, and the challenges associated with its operations.
- learn about the working mechanism of 3-phase and 1-phase induction motors, their applications, torque-speed characteristics, controlling motor characteristics by employing certain mechanisms.
- describe the working principle of Alternator and synchronous motor. Students learn how to operate different types of AC/DC machines.
EEE 363L Electrical Machines Lab
| Code and Name |
EEE 363L Electrical Machines Lab |
| Type |
Core, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1 |
| Pre-requisites |
EEE 241 |
Course Summary: Working principles and applications of various DC and AC machines such as Dc generator/motor, Alternator, Synchronous motor, Induction motor and transformer, Armature winding diagram, Torque-Speed characteristics, power flow diagram, Parallel operation of generator, House diagram, and controlling motor characteristics.
Course Objectives: The objectives of this course are to
- make students conversant with the concepts of various types of electrical machines and their applications.
- explain the operation principle of transformer. .
- gain knowledge about the principle of operation of DC generator and their constructions, and the challenges associated with its operations.
- learn about the working mechanism of 3-phase and 1-phase induction motors, their applications, torque-speed characteristics, controlling motor characteristics by employing certain mechanisms.
- describe the working principle of Alternator and synchronous motor. Students learn how to operate different types of AC/DC machines.
CSE 498/EEE 498/ETE 498 Internship/Co-op/Directed Research
| Code and Name |
CSE 498/EEE 498/ETE 498 Internship/Co-op/Directed Research |
| Type |
Required |
| Credit Hours |
0 |
| Pre-requisites |
Completion of 80 credits |
Course Summary: This course is designed to provide experience to students through internship/Co-op works in the public and private industry related to Electrical, Electronics, Telecommunication, and Computing Technology or through advanced research in relevant academic fields. Students will work there, prepare detailed report and present in front of a departmental committee.
Course Objectives: The objective of this course are to:
- Gain practical experience within the industry environment.
- Acquire knowledge of the industry in which the internship is done.
- Apply knowledge and skills learned in the classroom in a work setting.
- Develop a greater understanding about career options while more clearly defining personal career goals.
- Develop and refine oral and written communication skill
- Identify areas for future knowledge and skill developments.
CSE499A/EEE499A/ETE499A – Senior Design I
| Code and Name |
CSE499A/EEE499A/ETE499A Senior Design I |
| Type |
Required, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1.5 |
| Pre-requisites |
Completion of at least 100 credit hours including all the major core courses, math and science courses, Ethics, Language and Communication related courses. |
Course Summary: This is a senior level course, after a student has completed all the required major core courses, core math, and core science courses. This “capstone design course” involves multidisciplinary teams of students who build and test custom designed systems, components or engineering processes. Design projects selected from problems submitted by the students, faculty and local industry; Industry projects are given preference as they are best suited for meeting the course objectives; Instructional phase includes (not limited to): communications, report writing, visual aids, design process (requirements/specifications/objections, synthesis/analysis, design evaluation, implementation, maintainability, manufacturability, economic and social influences etc.), proposal preparation, estimating, project management and scheduling, contracts etc.; Performance phase includes (not limited to): design team formation and organization, design proposals, implementation of design process, project scheduling and management, design reviews, design simulation and testing, preparation of documentation, drawings, specifications, etc., written and oral presentation of completed projects.
Course Objectives: The objective of this course are to
- identify an engineering and/or computing problem, build appropriate strategy to solve the problem in a systematic way with given constraints of resources, budget, time etc.
- design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints
- use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice.
- identify the usability, manufacturability, and sustainability of a system/subsystem that is going to be developed under the project
- create an environment to work effectively in a group on multidisciplinary project to accomplish a common goal
- identify and validate the impact of economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety considerations and constraints in the project development phases.
- demonstrate engineering/computing project development phases through various written reports such as project proposal, time-line chart, requirement analysis report, design reports, final reports, etc.
- demonstrate an understanding of ethical and professional responsibility in a project development phases
CSE499B/EEE499B/ETE499B – Senior Design II
| Code and Name |
CSE499B/EEE499B/ETE499B Senior Design II |
| Type |
Required, Engineering, Lab |
| Credit Hours |
1.5 |
| Pre-requisites |
Completion of CSE499A/EEE499A/ETE499A – Senior Design I |
Course Summary: This is a senior level course, after a student has completed all the required major core courses, core math, and core science courses. This “capstone design course” involves multidisciplinary teams of students who build and test custom designed systems, components or engineering processes. Design projects selected from problems submitted by the students, faculty and local industry; Industry projects are given preference as they are best suited for meeting the course objectives; Instructional phase includes (not limited to): communications, report writing, visual aids, design process (requirements/specifications/objections, synthesis/analysis, design evaluation, implementation, maintainability, manufacturability, economic and social influences etc.), proposal preparation, estimating, project management and scheduling, contracts etc.; Performance phase includes (not limited to): design team formation and organization, design proposals, implementation of design process, project scheduling and management, design reviews, design simulation and testing, preparation of documentation, drawings, specifications, etc., written and oral presentation of completed projects.
Course Objectives: The objective of this course are to:
-
- familiarize students with the fundamental principles involved in the design process by doing a real design that solves a real world problem.
- make students able to identify and define problems.
- acquaint students with mechanisms of technological problem-solving, design alternatives, and project planning, implementation, and proper documentation.
- analyze the influence of cost, material resources, performance criteria, and relevant ethical and safety issues.
EEE 422/ETE 422 Principles of Digital Communications
| Code and Name |
EEE 422 Principles of Digital Communications |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Digital modulated signal and their spectral characteristics, PCM, the baseband and bandpass modulation, demodulation, coherent/non-coherent detection methods (and receiver structures) in AWGN channel, their error performance, communication over band-limited channels with ISI and AWGN, Matched filter, link budget, introduction to source coding, channel coding, spread-spectrum and multiple access techniques.
EEE 424 Mobile and Wireless Communication System
| Code and Name |
EEE 424 Mobile and Wireless Communication System |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Fundamental theory and design of high capacity wireless communications systems. This course will discuss cellular systems as well as high-speed wireless data communication systems. Topics include trunking, propagation, frequency reuse, modulation, source coding, error correction coding, multiple access schemes and equalization. Prerequisite: EEE 422
EEE 426 Fiber Optic Communication System
| Code and Name |
EEE426 Fiber Optic Communication System |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
4 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Optical Fibers-Basics; Telecommunications and Fiber Optics; Optical Fiber Waveguides; Fabrication, Cabling, Installation; Light Sources, Transmitters and Receivers; Components of Fiber-Optic Networks; Passive Components, Switches, Transceivers, WDM and DWDM systems, SDH Systems, FDDI, and Functional Modules of Fiber-Optic Networks-Telephone and Computer Networks, Networks, Protocols, and Services, OSI, SONET, ATM Networks and Layers; Broadband Communication System, Submarine Cable Networks, Applications and Future Developments. Mandatory Lab.
EEE 427 Satellite Communication System
| Code and Name |
EEE 427 Satellite Communication System |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
This course covers the most relevant aspects of satellite communications, with emphasis on the most recent applications and developments. The course covers the basic concepts of satellite communications, the orbital aspects, with emphasis on the geostationary orbit, Satellite subsystems, launching methods, and on-board processing. The design of a digital satellite link is discussed in detail, including link budgets, modulation, error control coding, baseband signaling theory, and multiple access methods. Frequency assignments and propagation aspects that affect the satellite link are then discussed. Antennas and earth station technology are presented, including the design of very small aperture terminals (VSATs). The course then covers non-geosynchronous orbits and their applications. Specific applications of satellites are also explored, including the global positioning system (GPS), satellites for mobile communication, and satellites for internet.
EEE 428 RF and Microwave Engineering
| Code and Name |
EEE 428 RF and Microwave Engineering + IL (*ETE 428) |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Review of Electromagnetic and circuit theory, Transmission line theory, waveguide, Planar transmission line design and measurement, Microwave network, Impedance matching and tuning, Passive microwave circuits, Active microwave circuits, RF-Microwave systems design.
EEE 493 Special Topics
| Code and Name |
EEE493 Special Topics |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Students can work for a Semester on an advanced topic in the area of Electronics or Telecommunication under the guidance of a faculty member. Prerequisite: Consent from the department chair and the concerned faculty
EEE 331 Data Communications & Networks
| Code and Name |
EEE 331 Data Communications & Networks |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Introduction to International Standards Organization open System Interconnection (ISO-OSI) reference model, design issues and protocols in the physical layer, data link layer and network layer; architectures and control algorithms of local area networks, point-to-point networks and satellite networks; standards in network access protocols; models of network interconnection, and overview of networking and communication software: This course has mandatory laboratory sessions every week.
EEE 421 Stochastic Signals and Systems
| Code and Name |
EEE 421 Stochastic Signals and Systems |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Engineering applications of probability theory, random variables and random processes, topics include: Gaussian and non-Gaussian random variables, correlation and stationary of random processes, time and frequency response of linear systems to random inputs using both classical transform and modern state space techniques. Ref: (1) Fundamentals of Stochastic Signals, Systems and Estimation Theory: With worked Examples by Branko Kovacevic and Zeljko Durovic (2) Random Signals and Systems (Prentice Hall Signal Processing) by Bernard Picinbono
ETE 423/EEE 423 Principles of Telecommunication Network
| Code and Name |
EEE 423 Principles of Telecommunication Network |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
ETE 331 or consent from Instructor |
Architecture, technology, operation, and application of telecommunication networks including digital telephony, access networks, fiber optic networks, data networks, ATM, SDH, FDDI and integrated services networks. Design and analysis of networks for voice, data, and video applications.
EEE 451 Telecommunications Business and Management
| Code and Name |
EEE 451 Telecommunications Business and Management |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Overview of management, business operations, technologies and industries of telecommunications.regular and value added voice and data services and business development, VoIP technoloogy, telecommunications market, industry, competitions, cost, pricing and tariff structure, regulation and compliance, interconnections, spectrum management, competition, restructuring and reengineering, class exercises of business technology strategy, business modeling, telecommunications business case analysis.
EEE 471 Digital Signal Processing
| Code and Name |
EEE 471 EEE 471 Digital Signal Processing |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Continuous- and discrete-time system theory.Block diagrams, feedback, and stability theory. Discrete-time stability, difference equations, Z-transforms, transfer functions, Fourier transforms, and frequency response. Analysis, design, and realization of digital filters. Discrete Fourier Transform algorithms, digital filter design procedures, coefficient quantization, finite word length arithmetic, fixed point implementation, limit cycles, noise shaping, decimation and interpolation. This course has mandatory laboratory sessions every week
EEE 495 Special Topics
| Code and Name |
EEE 495 Special Topics |
| Type |
Elective |
| Credit Hours |
3 |
| Pre-requisites |
None |
Students can work for a Semester on an advanced topic in the area of Electronics or Telecommunication under the guidance of a faculty member. Prerequisite: Consent from the department chair and the concerned faculty